Internal Control System
On April 19, 2006, ITOCHU's Board of Directors established the Basic Policy regarding the Internal Control System, which was most recently partially revised as of May 8, 2024. ITOCHU intends to revise and improve the internal control system tirelessly in order to build a system that is even more appropriate and efficient.
The following highlights two noteworthy initiatives under this policy.
Initiatives to Further Enhance the Reliability of Financial Reporting
We have established an internal system in order to further enhance the reliability of our consolidated financial reporting. The designing and implementing of internal control are periodically assessed to keep making appropriate improvements. Specifically, a Chief Responsible for Internal Control has been appointed in each organization to design and implement internal control. The Internal Audit Division evaluates the effectiveness of internal control and provides feedback to each organization to ensure the continuous improvement. Overall management of these initiatives is conducted by the Internal Audit Division, and important matters are determined through deliberations in the Disclosure Committee chaired by the CFO. In this way, we are working to reinforce the companywide internal control system.
Strengthening Risk Management on a Group Basis, Including Subsidiaries
ITOCHU has established internal committees and responsible departments in order to address the various risks associated with the Group's business operations, such as market risk, credit risk, country risk, and investment risk. At the same time, on a Group basis ITOCHU has developed the risk management systems and methods to manage various risks individually and on a companywide basis.
Those include a range of management regulations, investment criteria, risk exposure limits, and transaction limits, as well as reporting and monitoring systems. Moreover, ITOCHU regularly reviews the effectiveness of its risk management systems. As part of such efforts, the ALM Committee protects the ITOCHU Group's assets through deliberations on Group balance sheet management as well as analysis and management of risk.
Process for Investments
![[図]](/en/img/ab08_im01_2407en.jpg)
Managing Concentrated Risks
We also manage overall country risk exposure to non-industrialized countries and manage individual country risk based on internal country rating standards. Country limits are deliberated by the Asset Liability Management (ALM) Committee and approved by the HMC.
Business Continuity Plan (BCP)
Policy and Basic Concept
ITOCHU Group has established a Business Continuity Plan (BCP) to ensure that, even in the event of unforeseen circumstances—including major natural disasters such as large-scale earthquakes, widespread infectious disease outbreaks, incidents arising from terrorism, which may be triggered by international armed conflicts or geopolitical disputes, major accidents, and cybersecurity incidents including cyberattacks—critical business operations are either not interrupted at all, or, if interrupted, are restored in the shortest possible time.
Structures and Systems
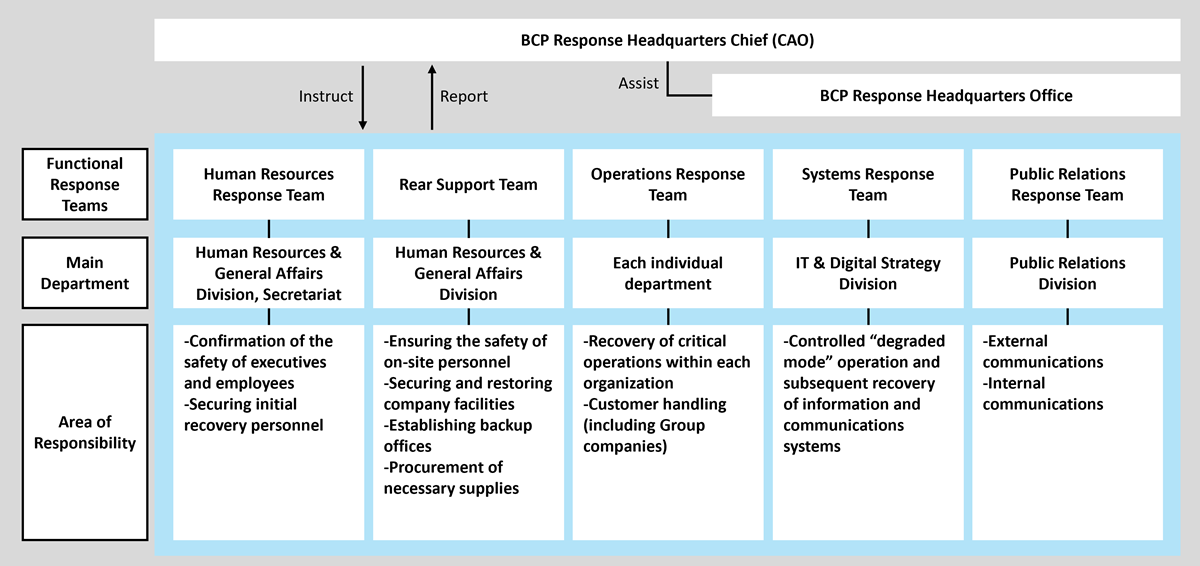
Within ITOCHU Group, under the leadership of the BCP Response Headquarters Chief (CAO), the BCP Response Headquarters Office plays the central role in updating the BCP and monitoring the status of BCP measures. In order to brace for rapidly changing unexpected situations, new policies and updates to the BCP are formulated as needed with CAO approval. These updates are then reported, based on their significance, to the Internal Control Committee and to the Board of Directors to further strengthen the BCP measures.
Furthermore, each business segment and administrative division designates a BCP representative who is responsible for formulating an individual BCP. Such individual plans compile the list of critical operations, the designated responsible persons, and the initial recovery personnel specific to that organization. In cases where a rapid response is essential due to large‐scale disasters or similar incidents, the overall business continuity plan together with the individual BCPs serve as the basis for ensuring employee safety and for maintaining the stability of business operations.
BCP Response Headquarters organizational chart (for a large-scale disaster)
Initiatives
Response in the Event of a Major Disasters
In the event of a major disaster, the response is structured into four distinct phases, gwith specific commanders and corresponding action items established in the plan:

1. Initial Recovery Actions
Confirm the safety of all executives and employees. This is carried out using available communication devices such as satellite phones, disaster-priority lines, computers, and mobile phones (via email or dedicated applications).
Inspect the damage to office facilities and initiate restoration work on both the buildings and installed equipment. In the event that Tokyo headquarters is impacted, Osaka headquarters is to be established as a backup office, while additional alternate office locations are also secured.
Provide for employees who cannot return home. In line with the ordinance for stranded individuals, each location is equipped with sufficient stocks of water, food, and emergency disaster supplies to allow occupants to remain in the office for approximately three days.
2. BCP Activation, 3. Business Recovery, and 4. Full Recovery
When the BCP Response Headquarters Chief
decides to activate the BCP, the BCP Response Headquarters is immediately convened to implement business recovery measures.
The process initially emphasizes the restart of the highest-priority operations; subsequently, the scope of operations is expanded in stages until normal, routine operations are restored.
Response in the Event of a Major Infectious Disease Outbreak
During the outbreak of large-scale infectious diseases—including, for example, the novel coronavirus—the company establishes a crisis management system tailored to the phase of infection spread. Under this system, ensuring the safety of employees and preventing further spread of infections are treated as top priorities. Simultaneously, ITOCHU Group works to contribute to societal stability through the maintenance of supply chains across its various business segments. In this manner, even during periods of widespread infection, a framework is constructed that enables the continuous execution of critical operations while mitigating risk.
Measures to Ensure the Effectiveness of the BCP
- Securing and Establishing Backup Offices for Emergency Business Operations
In addition to Tokyo and Osaka headquarters, the company’s employee dormitory at Hiyoshi is prepared and prioritized as a backup office to support the continuation of critical operations during emergencies. - Establishment and Regular Inspection of the BCP Response Headquarters Setup
The BCP Response Headquarters is organized so that it can be set up remotely in the event of an emergency. All systems required for remote setup are subject to regular inspection to ensure that they remain fully operational at all times. - Regular BCP Drills
BCP Response Headquarters members conduct regular training exercises. By simulating various scenarios each year, the company aims to enhance both crisis awareness and comprehensive crisis response capabilities.
Safety Measures for Employees on Travel or Stationed Overseas
Labor safety and health management at ITOCHU Group is undertaken with the Chief Administrative Officer (CAO) serving as the Chief Health Management Officer and is promoted under the supervision of the Human Resources and General Affairs Department, which is responsible for managing labor safety and health in each division company, headquarters, and overseas blocs.
ITOCHU Corporation operates worldwide with roughly 800 employees stationed overseas. We also send as many as ten thousand people a year on overseas business travel (data before the COVID-19 pandemic). Therefore, we are also working to offer health management to overseas staff to establish an environment where they can demonstrate their abilities with peace of mind even in unfamiliar situations, including situations where international armed conflicts or geopolitical disputes may affect local business operations or impact expatriates and travelers. Since close communication between overseas locations and Japan is vital to overseas security management, we have stationed overseas safety specialists at our headquarters. They regularly exchange information about politics, economics, public safety and other factors with personnel and general affairs representatives assigned to each of the six blocs worldwide. They then disseminate appropriate measures internally and to group companies. We have also established a system to cover regions where information is more difficult to obtain through contracts with international security consulting firms. In addition, we have been conducting overseas crisis response training in-house since FYE 2020. We mainly provide this training to those who we plan to station in countries and regions with poor security and employees who we expect to frequently send on business trips to such countries and regions.
Initiatives in Business Activities
To prepare for natural disasters, human-caused disasters, geopolitical risks, etc., we have been consistently working on diversifying our procurement sources and expanding the scope of our sales activities, with the aim of stabilizing our business operations. We believe that these efforts also serve as measures to address long-term risks.
