ITOCHU Announces Commercialization of World’s First CNF Koto Picks with a Timbre Close to Ivory
November 14, 2022
ITOCHU Corporation (headquartered in Minato-ku, Tokyo; Keita Ishii, President & COO; hereinafter “ITOCHU”) announced today that, in collaboration with RISHO KOGYO CO., LTD. (headquartered in Osaka-shi, Osaka; Mikio Tokura, President; hereinafter “RISHO KOGYO”) and Mishimaya Gakkiten Co., Ltd. (headquartered in Nagaoka-shi, Niigata; Kyoichi Yamada, President; hereinafter “Mishimaya Gakkiten”), it has commercialized the world’s first cellulose nanofiber koto picks (hereinafter “CNF koto picks”) that can create a timbre close to that of ivory picks.
Cellulose nanofiber (CNF) is a material made from processing cellulose, the main component of plants, to break it down to a nanometer size (nano = 1/1 billion). The raw materials for CNF are derived from wood, which can be supplied sustainably, and are extremely lightweight and strong, being one-fifth the weight of steel and five times as strong. In the Ministry of Economy, Trade and Industry’s preliminary calculations, a one trillion yen market is expected to be created for related materials by 2030.
CNF molded plates are lightweight, strong plates formed of CNF using RISHO KOGYO’s special technology. They have almost the same strength as aluminum with only about half its weight, and are expected to be put into practical use as a construction and structural material. ITOCHU and RISHO KOGYO focused on the fact that CNF molded plates have a texture similar to ivory, and began joint development of a material to replace ivory.
Ivory has been used for piano keys and a variety of other uses, but since the international ivory trade was banned with the 1990 Washington Convention, plastic products have come to replace many of the uses for ivory. In Japan, domestic trade of ivory continues to be allowed only under control based on laws and regulations, as there was no suitable alternative material for uses requiring the acoustic properties of ivory, which includes Japanese instrument parts. There are concerns, however, that it may become difficult to obtain ivory in the future.
The CNF koto picks that are being commercialized are sold after Mishimaya Gakkiten processes special CNF molded plates (Resin impregnation)*1 developed by RISHO KOGYO with conventional ivory processing technology. They have been assessed to create a timbre close to that produced by ivory*2, and will be available at Japanese music stores across Japan and on Mishimaya Gakkiten’s online store as products to replace ivory koto picks which are difficult to obtain. As the CNF molded plates can be processed using conventional ivory processing technology, we will continue to look into commercialization of the plates for parts of other Japanese instruments that favor ivory, such as shamisen plectrums.
One of the basic policies of ITOCHU's medium-term management plan is to "enhancing our contribution to and engagement with the SDGs through business activities,", and in addition to the development of CNF koto picks, ITOCHU is also progressing with the development of CNF construction materials*3 and other industrial applications with DAIKEN CORPORATION, a company it has invested in. ITOCHU will contribute to the social implementation of technical innovation of wood-derived materials that can be sustainably supplied, and will also contribute to the development of a rich society through a reduction in environmental impacts.
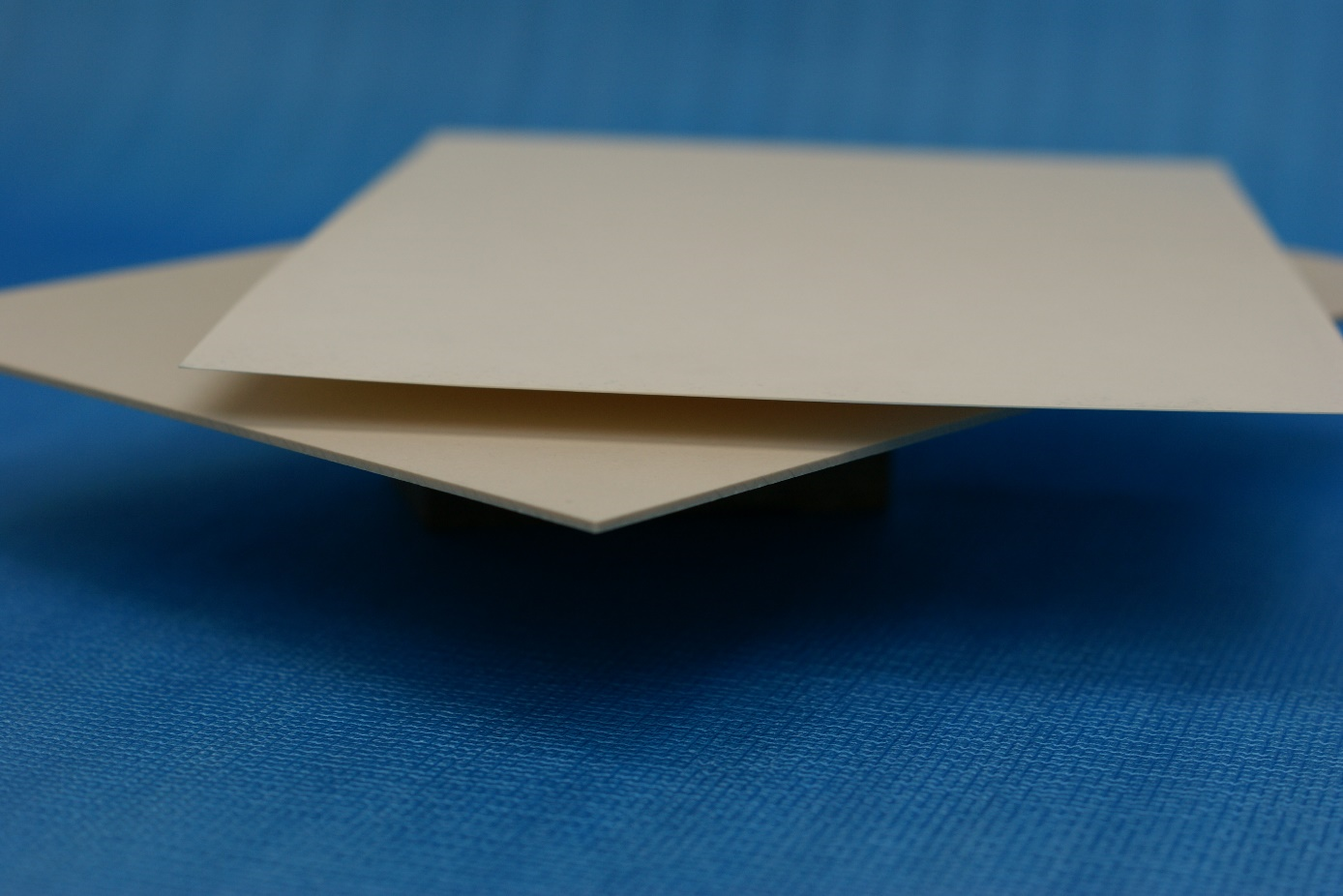
CNF koto picks and Ivory koto picks
|
CNF koto picks |
Ivory koto picks |
- *1Resin is impregnated in plate made mainly from CNF. Persons sensitive to resin should refrain from use.
-
*2Based on Mishimaya Gakkiten’s assessment.
Mishimaya Gakkiten is a long-established Japanese musical instrument shop founded as Yamadaya Shamisen ten informer Santo-gun in Niigata Prefecture in the Edo Period. Currently, in addition to its headquarters in Nagaoka-shi, Niigata, it has a factory in Fukuyama-shi, which leads Japan in its production of koto, and it produces and sells traditional Japanese taiko drums, shamisen, and koto. It also possesses extensive knowledge of the acoustic characteristics of materials for Japanese instruments, having long used plastic in place of ivory for a material for instrument parts.
・Mishimaya Gakkiten website: http://3408.co.jp/product.html (Japanese)
・Mishimaya Gakkiten’s e-commerce site: https://www.rakuten.co.jp/mishimaya3408/ (Japanese) - *3 “Development of Interior Building Materials Using Cellulose Nanofiber Technology” Selected as a NEDO-subsidized Project: https://www.daiken.jp/news/detail/20200901161840.html (Japanese)
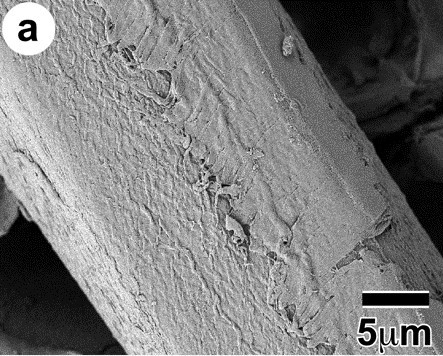
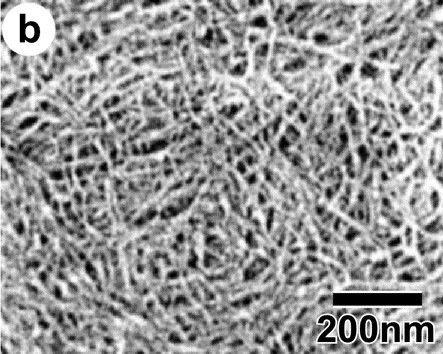
Cellulose fibers (a) and CNF (b)
|
Cellulose fibers |
CNF |
(provided by Professor Hiroyuki Yano, Kyoto University)
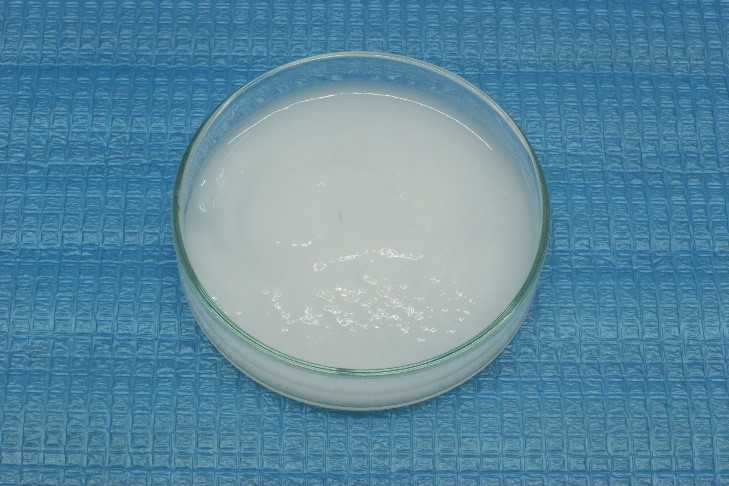
CNF (slurry state) and CNF molded plate
|
CNF (slurry state) |
CNF molded plate |