Prevention of Pollution and Resource Circulation
Policy and Basic Concept
Prevention of Pollution
Within its business activities, ITOCHU will strive to prevent and reduce environmental pollution caused by chemical substances, oils, and marine plastic waste, reduce emissions of air pollutants, and reduce and properly process hazardous waste and wastewater. We will fulfil our responsibility of pollution prevention by complying with international declarations, agreements, and treaties, as well as with the laws and regulations of the countries and regions in which we operate. We shall also comply with any other agreements that we have consented to.
Resource Circulation
ITOCHU handles a wide range of products, from plastics to metals, rubber, cement, and foodstuffs. We have identified “Ensure Stable Procurement and Supply” and “Address Climate Change (Contribute to a Decarbonized Society)” as ones of our key sustainability material issues. We will contribute to the formation of a circulating society with our business investees and stakeholders in the value chain of the products we handle to reduce the procurement of raw materials that have a negative impact on the environment and natural capital, and to promote resource circulation. We aim to realize resource circulation through the 3Rs (Reduce, Reuse, Recycle) and substituting sustainable raw materials from the design stage of products and services, and promoting sorting, collection, and recycling business for used products. We will actively work to procure raw materials and products with third-party certification for sustainability, with due consideration of appropriate use of natural capital, traceability, and consideration for local communities, etc.
Targets and Action Plan
ITOCHU sets qualitative management targets and quantitative performance targets to promote better practices in pollution prevention and resource efficiency. The environmental targets and achievements in FYE 2025 are as follows:
Qualitative Targets
 Please scroll sideways.
Please scroll sideways.
| Item | Boundary | Target | FYE 2025 Results and Evaluation | |
| Prevention of Environmental Pollution and Compliance with Laws and Regulations | Risk Assessment for Investment and Financing Projects | ITOCHU Corporation |
Perform pre-investment/financing assessments based on the ESG Checklist, which includes environmental assessment criteria. |
Properly implemented |
| Raising Management Levels through Auditing | ITOCHU Group |
Conduct internal audits on environmental management systems to ensure compliance, improved environmental efficiency, and better overall management. |
Properly implemented |
|
| On-Site Investigations of Group Companies | ITOCHU Group |
Select appropriate Group companies and conduct on-site environmental management investigations for them. |
Properly implemented |
|
| Promotion of Awareness Activities | Raising Awareness of Laws and Regulations | ITOCHU Group |
Increase internal awareness on the Waste Management and Public Cleansing Act and the Soil Contamination Countermeasures Act, as well as other relevant regulatory developments by providing learning opportunities such as seminars and courses. We will also monitor and review participation/uptake rates of these trainings in relevant segments of the company. |
Properly implemented |
| Resource Conservation, Promotion of Resource Circulation, and Monitoring of Performance | Office Waste Reduction | ITOCHU Corporation |
Reduce waste and promote recycling in office activities in accordance with our EMS. |
Properly implemented |
| Paper Consumption Reduction Target | ITOCHU Corporation |
Reduce paper consumption by raising awareness of our targets internally. |
Properly implemented |
|
Quantitative Targets
 Please scroll sideways.
Please scroll sideways.
| Item | Boundary | Target Period | Target | Progress in FYE 2025 Against Targets | Assessment | |
| Prevention of Pollution | Serious Environmental Accident | ITOCHU Corporation*1 |
Every Fiscal Year |
0 Serious Environmental Accidents |
0 |
Achieved |
| NOx SOx Emission Concentration | TAKIRON TECH CO., LTD. |
Every Fiscal Year |
Suppress to a level 20% below the legal standard |
Achieved |
Achieved |
|
ITOCHU Ceratech Corporation |
Every Fiscal Year |
Suppress to a level 20% below the legal standard |
Achieved |
Achieved |
||
| Resource Circulation/ Waste Discarded |
Volume of Waste Discarded | Tokyo Headquarters*2 |
March 2031 |
29% Reduction Compared to FYE 2020 |
46% Reduction Compared to FYE 2020 |
Achieved |
| Recycling Rate | March 2031 |
More than 90% |
92% |
Achieved |
||
| Resource Conservation | Paper Consumption | ITOCHU Corporation*2 |
March 2031 |
33% Reduction Compared to FYE 2020 |
55% Reduction Compared to FYE 2020 |
Achieved |
- ITOCHU Corporation, Overseas offices, Group companies subject to compliance
- We are aiming to commence the rebuilding of the Tokyo Headquarters building in September 2026, but the details of the plan are still underway. Once the details of the relocation plan are finalized, we will set new targets based on the management status of the temporary location.
Action Plan
 Please scroll sideways.
Please scroll sideways.
| Risks | Opportunities |
|
|
 Please scroll sideways.
Please scroll sideways.
Structures and Systems
Governance
ITOCHU’s governance structure and systems to manage environmental and social risks, including pollution prevention and resource recycling, are as follows:
Refer to: Governance
Evaluation of Pollution Prevention and Resource Circulation in New Business Investment Projects
For business investment projects that ITOCHU undertakes, the impact of the project on society and environment is evaluated in advance using the ESG Checklist for Investments, a checklist that must be submitted when entering into new business investment projects. For example, it includes monitoring the status of pollution prevention and resource circulation. The project is then only undertaken upon confirming that there are no problems in the results of those investigations.
We consider ensuring stable procurement and supply to be a material sustainability issue. We work to effectively utilize and to ensure stable procurement and supply of resources according to demand in each country with consideration for the environment (e.g., biodiversity). In doing this, we are aiming for a circulating society.
Assessment of Pollution Prevention and Resource Circulation at ITOCHU Group
ITOCHU has been conducting annual on-site investigations for ITOCHU Group companies having relatively high environmental impacts since 2001 to strengthen our environmental risk management. Throughout the assessment, we engage with the senior management team to assess the company’s status of exhaust and wastewater, chemical handling, and waste disposal.
Assessment of Efforts on Pollution Prevention and Resource Circulation in the Value Chain
Assessment of Sustainability Risk in Products ITOCHU Handles
ITOCHU conducts a sustainability risk assessment for each new product we will handle. We use LCA* analytical methods to evaluate the impact the product will have on the environment and society, compliance with environmental laws and regulations, relationships with stakeholders, and more. This evaluation covers the stages of the product from the procurement of its raw materials to its manufacturing, use and disposal. If there is a significant nature-related risk in the value chain, such as environmental pollution or resource depletion, we subject that product to priority management. We then formulate and implement various regulations, procedure manuals, education on the specific work operational factors, and other measures.
- Life Cycle Assessment (LCA): This is the technique to assess the impact of one product on the environment in all stages of its lifecycle — from raw materials to manufacture, transportation, use, and disposal or reuse.
Sustainability Surveys for Suppliers
Each Company at ITOCHU and applicable ITOCHU Group companies select important suppliers based on certain guidelines, including high-risk countries, handled products, and handled amounts, to grasp the status of our suppliers. Those in charge of sales at each Company and those in charge at overseas subsidiaries and Group companies visit those suppliers and interview them. Those in charge also conduct sustainability surveys with questionnaires on important suppliers. We check the situation of initiatives for exhaust, wastewater, and waste treatment, and resource recycling efforts including energy and raw material conservation. We make continuous improvements by asking suppliers to address issues as necessary.
Management of Chemical Substances
The chemicals handled in the Chemicals Division are those that have potentially serious impacts on human health and the natural environment and have become subject to various laws and regulations that aim to ensure appropriate handling across the supply chain – including during manufacturing, sales, transportation, and storage. Furthermore, the appropriate management of chemicals is crucial from a business perspective for ITOCHU’s Chemicals Division as well as violations and cases of non-compliance can impact the regulatory approvals we require on certain products.
There is an international trend to minimize risks at every level of the entire supply chain of chemicals. Against this background, both advanced nations and developing nations have started to introduce new regulations and to make large-scale revisions to existing regulations. Consequently, the regulatory environment in the handling of chemicals is expected to become ever stricter in the future.
We recognize the importance of compliance with laws and regulations in addition to knowledge of products and the industry as a company that handles chemicals. Our basic policy is that each individual should engage in business in accordance with the requirements of laws and regulations upon correctly understanding the laws and regulations concerning the products that they are in charge of handling.
Compliance with Laws and Regulations in the Divisions Handling Chemical Substances

At ITOCHU, the Chemicals Division has cross-functional oversight of our management of chemical substances. This includes oversight of the sales departments that handle chemical substances, which sit within the Chemicals Division, as well as relevant subsidiaries that handle chemical substances. In addition, the Chemicals Division has oversight of any sales divisions and subsidiaries outside of their direct control if chemical substances are used.
We strive to comply with laws and regulations through a management method based on a combination of thorough inquiries to specialized external consulting organizations and the use of a centralized management system to track environmental legal compliance. The management system was developed internally in 2016 and allows us to confirm and record applicable laws and measures at the chemical substance level for each product. We also provide training and educational opportunities to relevant sales staffs, supplemented by e-learning materials and handbooks that summarize the main points of relevant laws.
The external consulting organization that we currently employ for chemical substance management is Techno Hill Co., Ltd. Techno Hill has comprehensive knowledge regarding the field of chemical substances and provides us with informed advice on management systems, applicable laws and regulations for each product, and general trends movements in the industry.
In order to maintain and improve the abilities of each person in charge at a high level, we distribute our own handbook on chemical-related regulations to all persons in charge. There are 32 laws and regulations covered in this handbook, each of which outlines important aspects of compliance requirements. The purpose of this handbook is to educate our employees, especially new recruits and sales personnel, on the laws and regulations specific to the chemical industry.
By taking these initiatives, in FYE 2025, there were no major violations caused (e.g., license suspensions).
Management Structure for Emergency Response and Accident Response
ITOCHU responds as below in accordance with our accident and emergency response regulations.
If an accident occurs during the handling or storage of toxic or hazardous substances, we respond as follows in line with the manual.
- We will make reports as necessary according to the emergency contact network. In addition, we will take prompt action to limit the risks caused by toxic and hazardous substances.
- In the event of splashing, leaking, outflow, seepage or penetration underground, we will immediately notify the public health center, police station or fire department to that effect when there is a fear of a risk to the health of an unspecified or large number of people. At the same time, we will take measures to prevent risks to health.
Initiatives
Introduction of Individual Initiatives
1. Reduce
Initiatives to Introduce Environmentally-friendly Packaging in FamilyMart Stores
FamilyMart Co., Ltd., a subsidiary of ITOCHU, has set goals of increasing the ratio of environmentally-friendly containers and packaging* to 60% by 2030 and 100% by 2050, as part of its efforts to curb plastic use in FamilyMart Environmental Vision 2050.
By changing the specifications of containers and packaging, FamilyMart is working to reduce the amount of petroleum-based plastics used in the raw materials of containers and packaging and to promote the use of environmentally-friendly materials. We will continue to work toward achieving our 2030 and 2050 targets with the understanding and cooperation of our suppliers and consumers.
- Containers and packaging made from materials including plant-based biomass plastics and recycled PET
Major Initiatives in Environmentally-friendly Packaging
| Details of Initiatives | Reduction in Use of Plastics |
|
Estimated reduction of about 4,750t per year |
|
Reduction of about 900t per year |
|
Estimated reduction of about 421t per year |
|
Estimated reduction of about 170t per year |
Effort to Reduce Plastics at Convenience Stores
In accordance with the Act on Promotion of Resource Circulation for Plastics that went into effect in April 2022 in Japan, FamilyMart has set a goal of reducing the amount of petroleum-based plastics use by FYE 2031 by 50% from FYE 2020 level, and is working to reduce the amount of plastic spoons, straws, and other items distributed to customers who purchase boxed lunches, desserts, beverages, and other items.
Results of Major Initiatives to Reduce the Use of Certain Plastic Products
| Start Year | Details of Initiatives | Reduction in Use of Plastics |
| 2021~ |
|
|
| 2022~ |
|
- |
|
|
|
| 2024~ |
|
|
Initiatives to Reduce Food Waste in Convenience Stores

FamilyMart Co.,Ltd. is working to reduce food waste by promoting the active sale of near-expiry foods through discounted sales (FamilyMart’s Eco Discount) for ready-to-eat products such as rice balls and boxed lunches. Starting in March 2025, FamilyMart is gradually changing the discount stickers nationwide from those displaying only the price to designs featuring teary-eyed characters and messages.
The results of a demonstration experiment conducted since October 2024 showed that changing the sticker design increased the purchase rate of discounted products by 5% points. If this approach is expanded to stores nationwide, it is expected to reduce food waste in stores by approximately 3,000 tons annually.
Going forward, FamilyMart will continue to actively promote new initiatives to reduce food waste by using behavioral psychology to approach consumers' awareness and emotions regarding food waste, encouraging changes in purchasing behavior.
Develop Environmentally-friendly Garbage Bags “nocoo”

Sanipak Company of Japan Ltd., a subsidiary of ITOCHU, has developed “nocoo” environmentally-friendly garbage bags that reduce CO2 emissions. The use of natural lime stone as a raw material for nocoo reduces plastic use by approximately 20% and reduces CO2 emissions during the manufacture and combustion of garbage bags by approximately 20% compared to 100% polyethylene garbage bags. In FYE 2025, sales of nocoo in the 47 prefectures of Japan totaled 6,316 tons, contributing to a reduction in plastic use of 1,515 tons and a reduction in CO2 emissions (when incinerated) of 4,100 tons.
With nocoo, we will continue to address environmental issues that are familiar to everyone, such as reducing CO2 emissions through regular garbage disposal.
Refer to: nocoo website![]() (Japanese only)
(Japanese only)
2. Reuse/Recycle
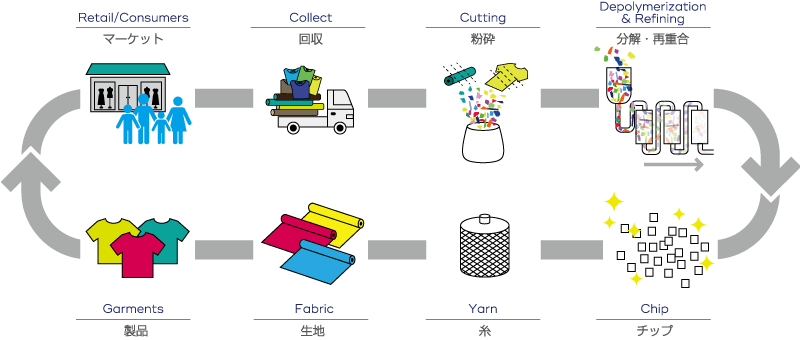
RENU® Project Aims to Realize Circular Economy

In the spring of 2019, ITOCHU launched a project called the RENU® project (“RENU”), which aims to address the issue of excessive waste in the fashion industry and realize circular economy. As its first product, we are developing recycled polyester made from textiles such as waste leftover fabric and used clothing. We will contribute to realize circular economy by developing this project through the entire supply chain of the fashion industry from raw materials to consumers.
Refer to: RENU® project website![]()
The environmental impact of handling recycled polyester at RENU project is as follows:
| FYE 2021 | FYE 2022 | FYE 2023* | FYE 2024* | FYE 2025* | |
| Feedstock equivalent to T-shirt (million pieces) | 3.5 |
6.0 |
6.3 |
6.5 |
5.5 |
| Reduced CO2 (t) | 521 |
893 |
1,931 |
2,010 |
1,715 |
| Reduced Water (kL) | 875 |
1,500 |
6,500 |
6,760 |
5,770 |
- Adopted LCA (FYE 2022 version)
Expansion of the Textile Collection Service for a Circular Economy
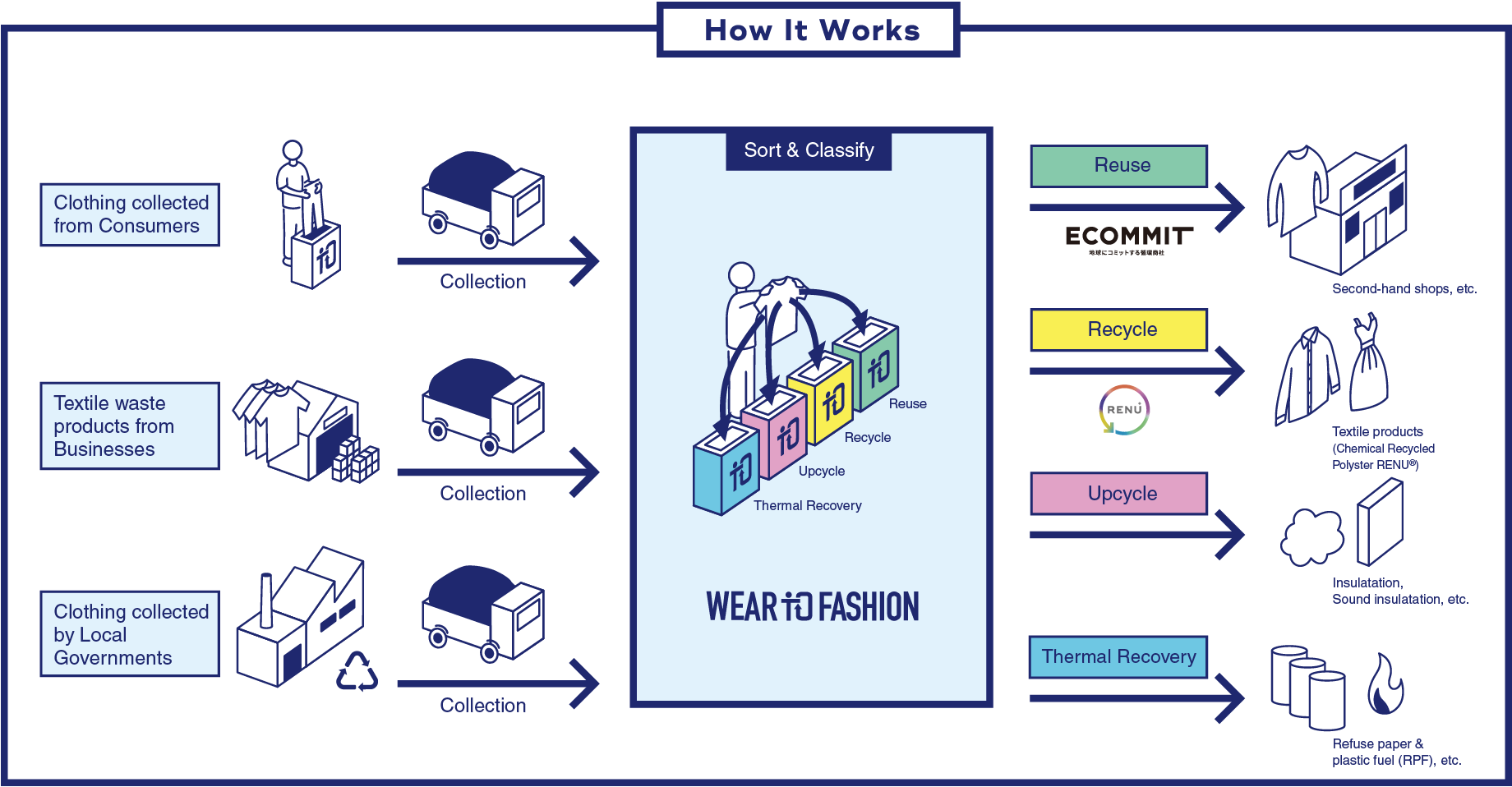
ITOCHU and ECOMMIT Co., Ltd., which develops resource circulation businesses through reusing and recycling, have signed an agreement to expand the textile collection service “Wear to Fashion” in the Japanese market. Starting spring 2022, the service will gradually be offered to all companies and local governments in Japan. As of March 2025, ITOCHU is collecting textiles from about 4,300 locations. We plan to collect approximately 8,900 tons of textiles in FYE 2026.
Additionally, utilizing the distribution infrastructure of the ITOCHU Group, a demonstration experiment was conducted from December 2024 to June 2025, where dedicated collection boxes for the resource circulation service "PASSTO" operated by ECOMMIT were installed in ten FamilyMart stores in Tokyo.
With this new initiative as a part of the RENU Project aimed at solving a problem in the textile and fashion industries, textile products coming out of various sites will be collected and sorted through combining our network in the textile and fashion industries and ECOMMIT’s system from collection to resource circulation. Reusable products will be reused utilizing ECOMMIT’s knowledge, and recyclable polyester products will be made into RENU. In doing so, the amount of discarded textile products will be reduced as much as possible and aims to realize a circulating economy.
ARChemia Project, a Recycling Project for Used Plastics and Textiles
In March 2023, ITOCHU signed a Memorandum of Understanding with Resonac Corporation regarding a joint study aimed at promoting a used plastic and textile recycling business. Based on this memorandum, we launched the ARChemia Project and began a collaboration to supply Resonac with recycled solid raw materials containing a mix of used plastics and textiles known as RPAF*1 and turn it into chemical products such as low-carbon ammonia with high environmental added value. We aim to increase the supply of RPAF to 10,000 tons in FYE 2028. Through the ARChemia Project, a joint project between chemicals and textiles, we will solve the social issue of waste and contribute to the development of circulating society.
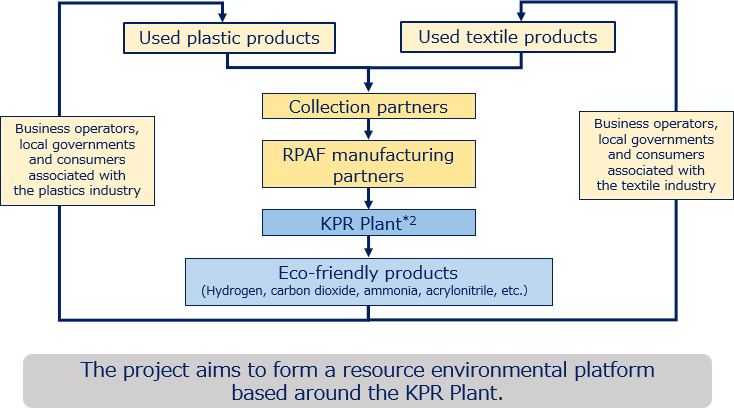
- RPAF: Refuse derived Plastics paper and Apparel densified Feedstock
A solid raw material for gasification-based chemical recycling adjusted for calorie generation, made mainly from used plastics, used paper and used textiles. - KPR Plant: Kawasaki Plastic Recycling Plant of Resonac
The Recovery of Nylon Waste to ECONYL® Nylon Products


ITOCHU and Aquafil S.p.A. have concluded capital and business alliance to promote and expand the businesses of circular nylon production.
Nylon is used for textiles and plastic materials made through petrochemistry in a range of fields such as fashion, carpeting, fishing nets, food packaging, and automobiles. However, many products use nylon blended with other materials in a compound form, making it a difficult material to be recycled.
In 2011, Aquafil created its ECONYL® Regeneration System that turns recovered nylon waste such as fishing nets, carpets and post-industrial waste back to caprolactam (CPL), a crude raw material. Through its proprietary chemical recycling technology, Aquafil eliminates impurities completely, to achieve regenerated nylon product having the same features of the virgin quality materials. ECONYL® nylon is made completely from waste, which enables up to 90% CO2 reduction compared to conventional nylon made from petroleum.
We will leverage on its ITOCHU Group’s diverse network and expand sales for applications in apparel, carpeting, automobiles, and packaging materials. In February 2022, YKK Corporation, which is a global leader in the manufacturing and sale of zippers, Aquafil and we are jointly developing environmentally-friendly recycled zippers and recycled buttons. In March 2024, we jointly developed fishing nets using ECONYL with Momoi Fishing Net Mfg. Co., Ltd. and Kinoshita Fishing Net Mfg. Co., Ltd. In October 2024, we announced a collaboration with Asahi Kasei Corporation to develop resin-based materials for 3D printers using ECONYL as the base polymer. By combining ECONYL with plant-derived raw materials, which Asahi Kasei has been developing, we will provide environmentally friendly materials to the market.
Moreover, we plan to enforce Aquafil’s nylon recovery scheme using its existing sales chain and will also implement the partnership from the perspective of the stable supply of raw materials to Aquafil. Through its collaboration from the recovery of waste to the sale of Aquafil’s products, we aim to expand the businesses of nylon circularity.
Development of Environmentally-friendly Flooring and Launch of Flooring Material Recycling Business

ITOCHU has launched the recycling business for flooring material together with the launch of DESSO, an eco-friendly flooring material produced by European construction material manufacturer Tarkett S.A., in the Japanese market in cooperation with Lilycolor CO., LTD., an interior design and decorating wholesaler.
Its new DESSO is an environmentally-friendly product based on recycling that enables the fiber surface part of the flooring material to be separated from the base material of the floor, making it possible to recycle the components. Since the start in 2024, DESSO has been adopted in dozens of properties.
This project aims not only to sell DESSO but also to contribute to the expansion of flooring material recycling through this collection and recycling scheme.
DAILITE, an Inorganic Board Utilizing Unused Resources and By-products
Daiken Corporation, a subsidiary of ITOCHU, developed DAILITE, the world's first new industrial material utilizing an unused resource Shirasu (volcanic ash) and a by-product of steel production Slag Wool, and started selling it in 1997. It offers performance characteristics such as lightweight, high strength, fireproof, breathability and good workability.
DAILITE combined with sheets and sliced veneer for surface decoration is used as the non-combustible and well-designed wall materials and louver materials. In addition, DAILITE has been adopted as a bearing surface for wooden houses, with a cumulative total of approximately 1.05 million homes as of the end of March 2023, according to Daiken's estimates.
In recent years, as the use of domestic and locally sourced timbers has been promoted in public buildings and other structures, the needs to use woods for interior wall and ceiling materials that required nonflammable properties are increasing. In this trend, Daiken has collaborated with locally sourced timbers from Tokyo and nine prefectures (as of May 2024), and non-combustible decorative panels and louver materials that combined DAILITE with locally sourced timbers are used in public facilities, station buildings, etc. Through the utilization of locally sourced timbers, the company contributes to the revitalization of local forestry.
Daiken will continue to develop products that contribute to sustainable resource circulation.


Wall panel: GLAVIO, a non-combustible panel made of DAILITE base material

The License Business of Polyester Chemical Recycling Technology
ITOCHU, Teijin Limited, and JGC Holdings Corporation have established a joint venture company, RePEaT Co., Ltd., to license technology for the chemical recycling of polyester products in January, 2023. In FYE 2026, the first licensed factory is scheduled to be completed in China with a capacity of 50,000 tons per year.
In response to urgent needs to counter global warming, the fiber and textile industry is working on measures, including the establishment of ecosystems for resource recycling, to address issues such as CO2 emissions from manufacturing processes and the mass disposal of used clothing. Currently, disposed textile products are used as a heat source (thermal recovery) or as raw materials for the production of other products (material recycling). Chemical recycling, however, is a revolutionary method of chemical decomposition for textile recycling that turns used textile products into new textile raw materials.
RePEaT will license recycling technology by taking advantage of Teijin’s proprietary chemical recycling technology, the expertise of JGC derived from its global engineering business, and our extensive network of textile industry players. Customers in Japan and other countries are expected to launch the cost-effective chemical-recycling business for the production of polyester materials.
In addition, RePEaT will provide consulting services to help customers establish ecosystems that collect used polyester fiber products for reuse as raw materials, thereby contributing to a more sustainable world through recycling.
Providing One-Stop Waste Management Services
Franchise companies with nationwide operations have traditionally disposed of waste on a small and decentralized scale on a store or area of franchise system basis, resulting in issues such as inefficiencies in labor and costs for each business and the risk of legal violations.
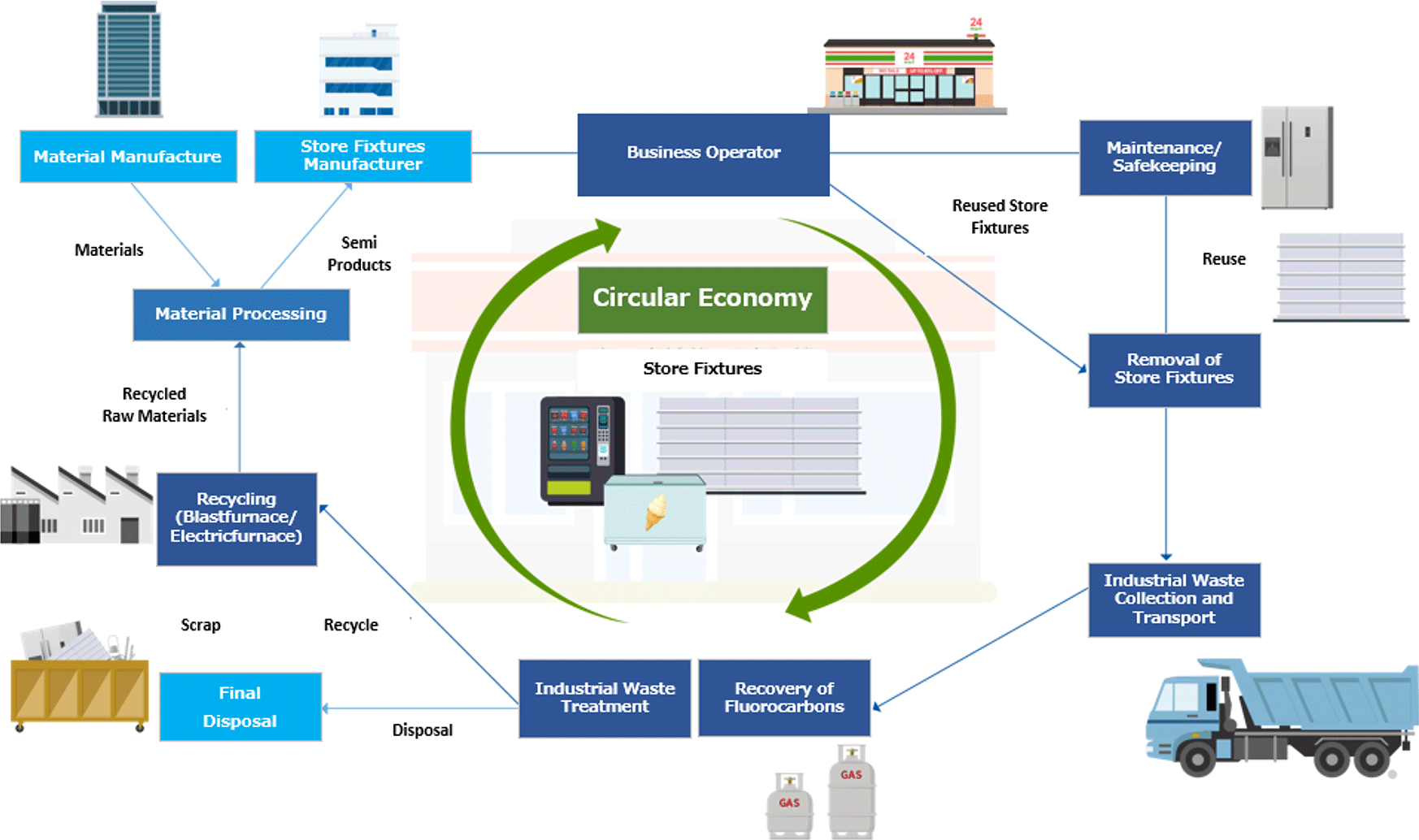
ITOCHU Metals Corporation (IMC) has established a recycling network centered on the ITOCHU Tetsugenkai, which consists of more than 100 excellent recycling companies nationwide, and provides a centralized management service, including IMC's own electronic manifest system, until waste is disposed of and recycled. This system helps to significantly reduce the risk of legal violations and disposal costs for waste generators, as well as improving recycling rates.
IMC currently provides a variety of services to support the initiatives of companies in various industries, including convenience stores, store fixture manufacturers, and beverage manufacturers, by offering a cross-industry recycling platform. In addition, IMC realizes the 3Rs by reusing waste materials that can be reused from the waste materials IMC is entrusted to manage at its maintenance sites, thereby contributing greatly to the formation of a circulating society.
Leading United Kingdom for Collecting and Recycling Casing Tyres

Murfitts Group Ltd, a company under ITOCHU subsidiary European Tyre Enterprise Limited, collects and processes casing tyres in the United Kingdom each year. Using the recovered material, it manufactures a range of recycled products such as rubber crumb products for sports surfaces, pathways, children’s playgrounds, carpet underlay, modified asphalt, and many other industrial applications. Its products are exported to markets across the globe.
Murfitts also has been developing and commercializing a proprietary pyrolysis technology, which decompose the tyre feedstock at high temperatures in a vacuum in order to recover various high-value materials such as carbon black and recycled fuel oil. This technology will help promote sustainability initiatives in the tyre industry by replacing one of major raw materials of tyres, carbon black, with a recycled product.
The Cooperative Development of Material Recycling Technology for Multi-layer Film Packaging
ITOCHU has entered into an agreement for cooperative development of material recycling technology for multi-layer film packaging with artience Co., Ltd. (former Toyo Ink SC Holdings Co., Ltd.)
In 2019, artience developed a technology to separate the ink, adhesive, etc. that make up the multi-layer film or packaging in cooperation with the world’s largest environmental solutions company. A demonstration pilot plant started operation at the end of 2022, and, moving forward with LCA appraisals, cost simulations, and other verifications. artience plans to start a post-industrial recycling business, and aim to start the business under commercially conditions as soon as possible. In addition to acquiring exclusive marketing rights in Japan and first refusal rights in Asia and Europe related to major product materials related to this technology, we will widely provide environmental solutions to food and consumer products company, retailers, brand owners, and more through requests to build structures for material recycling using this technology and to design recyclable, environmentally-friendly packaging.
Through this initiative, both companies will make currently unrecyclable multi-layer film packaging into a recyclable product, aiming for a more than 40% material recycling rate in Japan and abroad.
3. Renewable
Number One Trader in the World for the Cement Substitute of Blast Furnace Slag

Blast furnace slag is a by-product of the steelmaking process. As its property is similar to a cement, a blast furnace slag can substitute a cement. The benefits of using a blast furnace slag are, firstly, that it helps us save natural resources (e.g., limestone – the raw material of cement) and, secondly, that it enables us to cut CO2 emissions coming from cement manufacturing process. About 840kg of CO2 is reduced when a ton of cement is produced with using blast furnace slag.
ITOCHU has been selling blast furnace slags from Japan and other countries to all over the world for over 20 years and volume-wise, we are the No.1 independent blast furnace slag trader. As there is more call for carbon neutrality globally, a blast furnace slag will be needed even further. Our mission is to develop and keep a stable supply chain of blast furnace slag to end users and be a part of the global decarbonization efforts.
Collaboration to Introduce Renewable Biomass Polypropylene in the Japanese Market
Japan has formulated a basic strategy to introduce approximately two million tons of biomass-based plastic products by 2030 as a countermeasure against ocean plastic waste and climate change.
Since the agreement in 2020 with Borealis AG regarding the marketing of biomass polypropylene (bio-PP) derived from renewable resources in the Japanese market, ITOCHU has been working in collaboration with ITOCHU PLASTICS INC. to advance the deployment of food containers and packaging materials made from plant-derived resins with a market-oriented perspective. Specifically, since June 2021, we successfully had FamilyMart initially in Japan begin replacing some of its pasta containers made with bio-PP. We are also working on product development in various fields, primarily focusing on food containers, hygiene products, and daily necessities.
We have obtained ISCC PLUS certification for the domestic sales of synthetic resins derived from biomass resources manufactured by the mass balance method. This certification proves sustainable raw material procurement in a way that can be traced through the supply chain, and the portion of biomass raw material contributes to greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions reduction.
Collaboration with Outside Initiatives
Compliance with the Containers and Packaging Recycling Law
ITOCHU understands our own manufacturing and import volume of containers and packaging every year to recycle containers and packaging. We then pay a recycling fee to the Japan Containers and Packaging Recycling Association. The aim of this is to contribute to promoting the formation of a circulating society as a specified business operator prescribed by the Containers and Packaging Recycling Law.
The Recycling Fee We Pay Every Year
(Unit: Yen)
 Please scroll sideways.
Please scroll sideways.
| Fiscal Year | FYE 2020 | FYE 2021 | FYE 2022 | FYE 2023 | FYE 2024 | ||||||||||||||
| Recycling Fee/ Contribution Fee |
Recycling | Contribution | Total Amount | Recycling | Contribution | Total Amount | Recycling | Contribution | Total Amount | Weight (t) | Recycling | Contribution | Total Amount | Weight (t) | Recycling | Contribution | Total Amount | Weight (t) | |
| Glass Bottles | Colorless | 813,659 |
0 |
813,659 |
925,650 |
0 |
925,650 |
1,145,967 |
0 |
1,145,967 |
236.752 |
1,022,254 |
0 |
1,022,254 |
201.599 |
58,398 |
0 |
58,398 |
9.387 |
| Brown | - |
- |
- |
- |
- |
- |
- |
- |
- |
- |
114,234 |
0 |
114,234 |
13.314 |
2,446,217 |
0 |
2,446,217 |
289.594 |
|
| Other Colors | - |
- |
- |
- |
- |
- |
- |
- |
- |
- |
- |
- |
- |
- |
- |
- |
- |
- |
|
| PET Bottles | - |
- |
- |
- |
- |
- |
630 |
0 |
630 |
0.084 |
- |
- |
- |
- |
- |
- |
- |
- |
|
| Paper Containers and Packaging | 15,288 |
4 |
15,292 |
10,168 |
0 |
10,168 |
15,453 |
0 |
15,453 |
1.385 |
7,654 |
0 |
7,654 |
0.788 |
15,261 |
0 |
15,261 |
0.885 |
|
| Plastic Containers and Packaging | 1,463,900 |
4,537 |
1,468,437 |
2,432,519 |
0 |
2,432,519 |
2,739,244 |
0 |
2,739,244 |
52.383 |
2,167,099 |
0 |
2,167,099 |
41.583 |
3,149,074 |
0 |
3,149,074 |
61.743 |
|
| Total | 2,292,847 |
4,541 |
2,297,388 |
3,368,337 |
0 |
3,368,337 |
3,901,294 |
0 |
3,901,294 |
290.604 |
3,311,241 |
0 |
3,311,241 |
257.284 |
5,668,950 |
0 |
5,668,950 |
361.609 |
|
Food Recycling
ITOCHU makes regular reports on the amount of food we discard and the amount we recycle in Japan to comply with the Food Recycling Law. We are striving to suppress the generation of waste and to promote recycling (e.g., conversion into feed) in line with the reference rate (recycling rate target).
 Please scroll sideways.
Please scroll sideways.
| FYE 2021 | FYE 2022 | FYE 2023 | FYE 2024 | FYE 2025 | ||
| Quantity recycled | Amount of food waste generated (Unit: t) |
1,125.8 |
955.9 |
939.4 |
1,944.3 |
813.6 |
Amount of recycling |
775.5 |
762.0 |
854.6 |
1,747.6 |
759.4 |
|
Amount of disposal |
350.3 |
193.9 |
84.8 |
196.7 |
54.2 |
|
| Target (recycling rate target by individual food related operator) | Reference rate |
79.8% |
80.8% |
80.8% |
80.8% |
80.8% |
| Percentage recycled | Recycle rate*1 |
68.9% |
81.9% |
91.0% |
89.9% |
93.3% |
- Recycle rate is calculated as in below formula defined by the Ministry of Agriculture, Forestry and Fisheries.
(Amount of suppressed waste (vs FYE 2008) + Amount of recycling + Amount of heat recovery × 0.95 + Amount of weight reduction)/(Amount of suppressed waste (vs FYE 2008) + Amount of waste food generated)
- FYE 2026 recycling rate target: 80.8%
Initiative Participation (Activities Through Business and Industry Groups)
ITOCHU is participating in the Global Environment Subcommittee of the Committee on Environment and Safety – an environment and energy related committee of the Japan Business Federation (Keidanren). We are working to realize an environmental policy compatible with the economy (e.g., through promotion of voluntary action plans, and measures for global warming, waste and recycling and environmental risks including water management). We are also participating in the Environment Working Group of the Japan Foreign Trade Council. We are striving to build a decarbonized society, construct a circulating society, and to support environmental related laws and regulations. The goals set by the Environment Working Group are as follows:
Reduction Target for FYE 2026 in Domestic Business Activities (Trading Company Industry)
- Disposal Amount: Reduce 82% compared to FYE 2001
- Generation Amount: Reduce 62% compared to FYE 2001
- Recycling Rate: 83% or more