Risk Management
Policy and Basic Concept
ITOCHU Group is exposed to various risks due to its wide range of business natures, such as market, credit, and investment risks.
We acknowledge risk management as a key management issue. Therefore, we have established our basic risk management policy based on the concept of the COSO-ERM framework. We consider risks that could significantly impact our future financial condition and performance as important risks and regularly review them to identify key risks. The respective divisions responsible for each key risk (risk owners) manage them based on specialized expertise and report these risks to various risk committees and the Board of Directors. In this way, we have established a comprehensive, company-wide management system and methodologies for risk management.
Targets and Action Plan
| Risks | Opportunities |
|
|
Structures and Systems
Enterprise Risk Management System
ITOCHU conducts enterprise risk management by implementing a company-wide risk management system that includes ongoing risk management by the divisions responsible for key risks (first line), corporate headquarters risk management by HMC and risk management-related committees under the supervision of the Board of Directors (second line), and oversight of progress and the framework from an independent perspective by the Internal Audit Division (third line). This system is in line with the three-lines model recommended by the COSO-ERM framework. For ongoing risk management, each business segment manages risks within the scope of its delegated authority to facilitate prompt decision-making, with the risk-responsible divisions continuously monitoring the situation.
In this way, ITOCHU Group has established internal committees and responsible divisions in order to address the various risks associated with the Group’s business operations, such as market risk, credit risk, country risk, and investment risk. At the same time, on a Group basis ITOCHU has developed the risk management systems and methods to manage various risks individually and on a companywide basis. Those include a range of management regulations, investment criteria, risk exposure limits, and transaction limits, as well as reporting and monitoring systems.
In addition, the divisions responsible for key risks conduct Reviews of Consolidated Risk Management Action Plans every six months, reporting the management status for each key risk to the Internal Control Committee to periodically review the effectiveness of our management system. Furthermore, the regular review results for each key risk are reported by the respective risk officers to the Board of Directors.
At the corporate headquarters’ level, we established and implemented a system for reporting and reviewing individual cases and internal frameworks related to various risk areas through the HMC—which is composed of the Chairman/CEO, the President/COO, and the executive officers appointed by the President/COO—and its subordinate bodies, including the Internal Control Committee, Disclosure Committee, ALM Committee, Compliance Committee, Sustainability Committee, and Investment and Financing Committee, among others. The HMC is chaired by the President. The chairpersons of each committee are officers holding positions such as CFO, CAO, or CXO, and they approve and endorse the matters under deliberation. For significant issues, a mechanism is in place where the outcomes are decided by the President/COO and the Board of Directors, ensuring the appropriate and agile execution of operations.
For instance, the Sustainability Committee, one of the principal internal committees introduced above, is tasked to promote sustainability in the ITOCHU Group’s company-wide risk management. The Committee manages operational ESG risks such as human rights risks, health and safety risks, climate change risks, and natural disaster risks, as well as ESG risks related to investments. The Committee cooperates with other Committees as necessary and makes decisions on policies and initiatives to address ESG risks and the ways of promoting widespread understanding of those risk management system throughout our organization. Activities and findings are compiled by the Committee and reported to the Board of Directors annually.
Operational-level Risk Management System
At the individual Division Company level, each Company’s President reports to the Division Company Management Committee (DMC), an advisory body to the Companies. The DMC deliberates on important issues such as those regarding investments, lending, assurance, and business management that have the potential to substantially impact the management of each Division Company. If the risks identified or escalated exceed beyond the responsibilities mandated to the DMC, depending on the gravity of the risk and upon deliberation with other committees as necessary, risk issues may be escalated to the HMC and/or the Board of Directors.
Functions of the Board of Auditors and Internal Audit Division
ITOCHU is a company with Audit & Supervisory Board Members and endeavors to strengthen the monitoring/supervising function and ensure the transparency of decision making by fully empowering our Audit Board—which comprises two full-time auditors and three external auditors—to monitor the Board of Directors. Our auditors attend all Board of Directors meetings and, in an independent capacity, participate in each advisory and internal committee where they serve as members. In addition, the full-time auditors participate in other key meetings and listen to reports on the execution of duties from directors and other senior executives. By leveraging their specialized expertise and backgrounds to provide necessary feedback, they contribute to the maintenance and enhancement of governance reliability.
Our internal audit organization—Internal Audit Division, which is directly under the President—carries out audits on risk management divisions as well as on each Division Company and Group company from an independent standpoint. This division reports both to the Chairman/CEO and the President/COO, and also directly to the Executive Officers’ meeting attended by directors and auditors, thereby establishing a dual reporting line. Internal Audit Division works closely with the auditors by discussing the internal audit plan and by regularly exchanging views on audit results and any identified issues or recommendations.
Risk Management Governance Structural Chart (As of June 18, 2025)

- Internal Audit Division reports internal audit results directly to Chairman & CEO and President & COO, and to Executive Officers’ meetings where Members of the Board and Audit & Supervisory Board Members are present
Response to Significant Risks for ITOCHU and Reassessment of Emerging Risks
Regarding the risks that could significantly affect the future financial condition and performance of ITOCHU Group, Global Risk Management Division at our headquarters acts as the coordinator to conduct regular reviews of the 18 key risks outlined in our Basic Risk Management Policy. Specifically, these reviews are performed by comprehensively considering both the opinions of external experts consulted as needed and the content of the Reviews of Consolidated Risk Management Action Plan (Semi-Annual Review) conducted by the divisions responsible for each key risk on a semiannual basis.
For emerging risks, we collect information on potential new risks from the external experts and the Semi-Annual Review. We then examine whether additional measures are warranted by comparing the impact on our Group with that of the existing key risks.
The results of the reviews for both key and emerging risks are reported by each risk-responsible division to the Internal Control Committee. Following deliberation by the committee—chaired by the CAO—the CAO then reports to the Board of Directors on the establishment and operational status of the Basic Policy on Internal Control Systems.
Through these measures, our Group endeavors to fully comprehend both the risks and opportunities arising from macro-environmental factors such as economic downturn risks, geopolitical risks, and environmental and social risks. In doing so, we aim to pursue flexible responses and transformative changes to our business model in response to evolving management environments and temporal shifts, thereby ensuring stable supply procurement, enhanced business continuity, and the development of further competitive advantages.
Please refer to the PEST analysis in our Integrated Report![]() .
.
Response to Key Risks
The divisions responsible for each key risk are implementing risk mitigation measures, drawing on their specialized expertise, as described below. We have established systems to manage and monitor risks not only within individual and Group companies but also, depending on the circumstances, for business partners along the value chain and potential new investment candidates.
| Risk Item | Responsible Divisions (Managing Officer) | Leading Risks | Risk Mitigation Measures |
| Compliance Risks | Legal Division (CAO) |
Risks relating to compliance with various laws, ordinances and regulations |
Compliance officers in each organization (including companies) manage risks and give guidance on them based on the ITOCHU Group Compliance Program. |
| Legal Risks (Excluding Compliance Risks) | Legal Division (CAO) |
Risks from various regulatory restrictions and changes to laws, risks incurred from regulatory tightening and deregulation, risks incurred due to different administration and interpretation of legal systems, and risk of losses (compensation liability etc.) occurring due to disputes (lawsuits and complaints) |
Mitigate the risk of losses expanding by checking contracts and other paperwork in advance in relation to conflicts (lawsuits and complaints). Raise awareness about risks from changes to laws and ordinances by holding various courses. Respond to those risks by accepting inquiries on a case-by-case basis. |
| Risks Associated with Trade Security Policy Management | Legal Division (CAO) |
Risks relating to compliance with the Foreign Exchange and Foreign Trade Act (security-related) and risks relating to international security such as the legal regulations and sanctions of other countries |
Export Control & Sanctions Department performs centralized management. Perform appropriate management and give guidance in cooperation with the Export Control Program Officers in each Division Company or department. |
| Risks Associated with Customs | Legal Division (CAO) |
Risks relating to compliance with the three customs acts (Customs Act, Customs Tariff Act and Act on Temporary Measures Concerning Customs) |
Conduct in-house monitoring, provide training, accept inquiries on a daily basis, ensure employees and officers are aware of laws and ordinances, and hold periodic report briefings on customs in line with import customs clearance management and customs management manuals, and export customs clearance management manuals. |
| Country Risks | Global Risk Management Division (CFO) |
Risk of losses occurring due to the actions of nations themselves or the environment in which those nations have been placed |
Global Risk Management Division periodically aggregates the country risk exposure and discloses it as the outstanding balance of investments, loans and guarantees by major country. |
| Commodity Price Risks (Specific, Important Product) | Global Risk Management Division (CFO) |
Risk of losses occurring due to product market price fluctuations |
Set monetary amount limits, quantity limits and period loss limits. Periodically review compliance with those limits. |
| Credit Risks | Global Risk Management Division (CFO) |
Risk of losses occurring due to default on debts in contracts with associated companies |
Set credit amounts for each associated company and transaction type. In principle, review the credit amounts annually. |
| Investment Risks | Global Risk Management Division (CFO) |
Risks relating to new investment execution and existing business monitoring and exit decision-making |
Make decisions on new investments based on investment standards. Periodically monitor existing investments. Promote asset replacement by applying the EXIT selection standards on investments not worth holding. |
| Stock Price Risks | Global Risk Management Division (CFO) |
Risk of losses occurring due to stock price fluctuations |
Periodically grasp and monitor the amount of impact on consolidated shareholder’s equity due to stock price fluctuations. |
| Foreign Exchange Rate Risks | Finance Division (CFO) |
Risk of losses occurring due to foreign exchange rate fluctuations |
Mitigate risks through hedge transactions using futures exchange contracts and other derivatives. |
| Interest Rate Risks | Finance Division (CFO) |
Risk of losses occurring due to interest rate fluctuations |
Mitigate interest rate fluctuation risks by grasping the interest rate mismatch amount. |
| Financing Risks | Finance Division (CFO) |
Risk that it will no longer be possible to raise financing smoothly due to turmoil in the financial markets |
Ensure sufficient liquidity by using cash and deposits and commitment lines. At the same time, mitigate risks by diversifying financing sources and methods. |
| Information System and Security Risks | IT & Digital Strategy Division (CXO) |
|
|
| Labor Management Risks | Human Resources & General Affairs Division (CAO) |
Risks which may occur in labor management (long working hours, unpaid overtime, etc.) |
Based on occupational safety and health management, Division Companies and Headquarters human resources and general affairs staff summarize on-site inquiries and reports and then communicate them to the Human Resources and General Affair Division. Appropriately respond in consultation with legal advisors as necessary. |
| Human Resources Risks | Human Resources & General Affairs Division (CAO) |
Risks arising from shortfalls and outflow and securing management and operational human resources |
Secure diverse human resources. Continuously develop abilities including by cooperation between ITOCHU and Group companies. Place the right people in the right place by developing a rewarding working environment. |
| Risks Associated with the Appropriateness of Financial Reporting | General Accounting Control Division (CFO) |
Risks relating to securing reliability in financial reporting by preparing and disclosing appropriate financial reports |
Appoint a person in charge of collecting information on the new establishment, revision and abolition of accounting standards. Disseminate that information by issuing notifications, and posting on the Intranet and sending emails. |
| Risks Associated with Internal Control | General Accounting Control Division (CFO) |
Risk of incidents and fraud occurring due to employees and officers not performing operations in line with the rules and manuals relating to accounting |
Monitor internal control operations. |
| Environmental and Social Risks | Sustainability Management Division (CAO) |
Risks relating to compliance of environmental and social related laws and ordinances and promotion of key issues in sustainability |
Plan a system to grasp environmental and social risks in our company and value chains when starting and continuing trades and business investment operations, and to monitor the status of the response to those risks. Monitor in cooperation with other departments as appropriate. |
Initiatives
Risk Management Method
We conduct the following management throughout the year to build a PDCA cycle. We periodically move through the risk management cycle. Through these efforts, we are mitigating and preventing increasingly complex and diversifying risks.
- Plan: The divisions responsible for managing the 18 key risks formulate action plans to prevent and mitigate those risks every year (Reviews of Consolidated Risk Management Action Plans). They then comprehensively identify potential risks. After that, the Internal Control Committee discusses the risks which should be tackled and management policies. The CAO then approves those policies.
- Do: Take measures based on the management policies by each department responsible for key risks.
- Check: Compile the status of measures and the following term’s action plans every six months. Report the status and action plans to the Internal Control Committee.
- Action: Take improvement measures and additional measures.
Reviews of Consolidated Risk Management Action Plans
The divisions responsible for the 18 key risks conduct Reviews of Consolidated Risk Management Action Plan semiannually. In this review, each risk-responsible department—for example, those in charge of compliance risk, country risk, and foreign exchange risk—reports on the status of risk management documentation, systems, and action plans, as well as the measures being taken at the individual and subsidiary levels. Global Risk Management Division compiles these reports as the coordinator and submits them to the Internal Control Committee for periodic review of the effectiveness of our management framework. Furthermore, the risk officers responsible for each risk present the review results for each key risk to the Board of Directors.
Training
Executive Risk Management Skills
Our directors and auditors are comprised of individuals who possess risk management experience in both financial and non-financial areas. However, in light of the vast array of internal and external environmental changes and challenges faced by a general trading company, we provide opportunities—for instance, during Board meetings attended by all directors and auditors—to update their knowledge on external information and stakeholder demands that contribute to strengthening company-wide risk management.
Moreover, in order to promote Outside Directors’ and Outside Audit & Supervisory Board Members’ understanding of risk management and other ITOCHU Group initiatives, Outside Directors and Outside Audit & Supervisory Board Members have regular meetings with the Chairman & CEO and the President & COO; Outside Directors have regular liaison meetings with full-time Audit & Supervisory Board Members; and internal auditing units meet regularly with Outside Directors to report on their activities. Outside Directors and Outside Audit & Supervisory Board Members also meet regularly on an individual basis with Division Company Presidents and Officers in charge of overseeing head office functions. We also hold information sessions for Outside Directors and Outside Audit & Supervisory Board Members to provide opportunities to deepen their understanding of environmental, social, compliance, and various other risks as well as the related risk management systems.
Outside Directors and Outside Audit & Supervisory Board Members also receive pre-briefings before meetings of the Board of Directors, with explanations of individual investment matters that includes not only the investment details but also risk analysis and response; in so doing, we work to ensure that they enter meetings of the Board of the Directors with a full understanding of the relevant risks.
Employees’ Risk Management
Additionally, divisions responsible for risk management take the lead annually conducting activities such as informing all employees, including those in managerial positions, about risks that must be addressed and providing training on risk management. In recent years, we have implemented a broad range of training programs—covering everything from basic knowledge of business investments to learning from past failures—for employees at various levels. These sessions are conducted by Global Risk Management Division, by the divisions responsible for each risk, and by the companies themselves. In the case of companies, training tailored to specific industries or products is also provided for relevant stakeholders.
| Examples of training programs mandatory for all employee |
|
Risk Capital Management*1 and Management of Concentration Risk
Risk Assets and Risk Buffer*2

- The cost of shareholders’ equity set at 8%
- Risk Buffer = Total shareholders’ equity +
Non-controlling interests
Strict Management of Risk Assets
Our basic operational policy involves first calculating risk assets based on the maximum amount of possible future losses from all assets on the balance sheet including investments and all off-balance-sheet transactions. Second, we manage the amount of risk assets within the limits of our risk buffer (Total shareholders’ equity + Non-controlling interests). As we promote investments that will lead to evolve existing business moving forward, we will work to maintain risk assets within the limits of our risk buffer, conduct strict risk management, and further strengthen our financial position.
Business Investment Management
Fundamental Approach
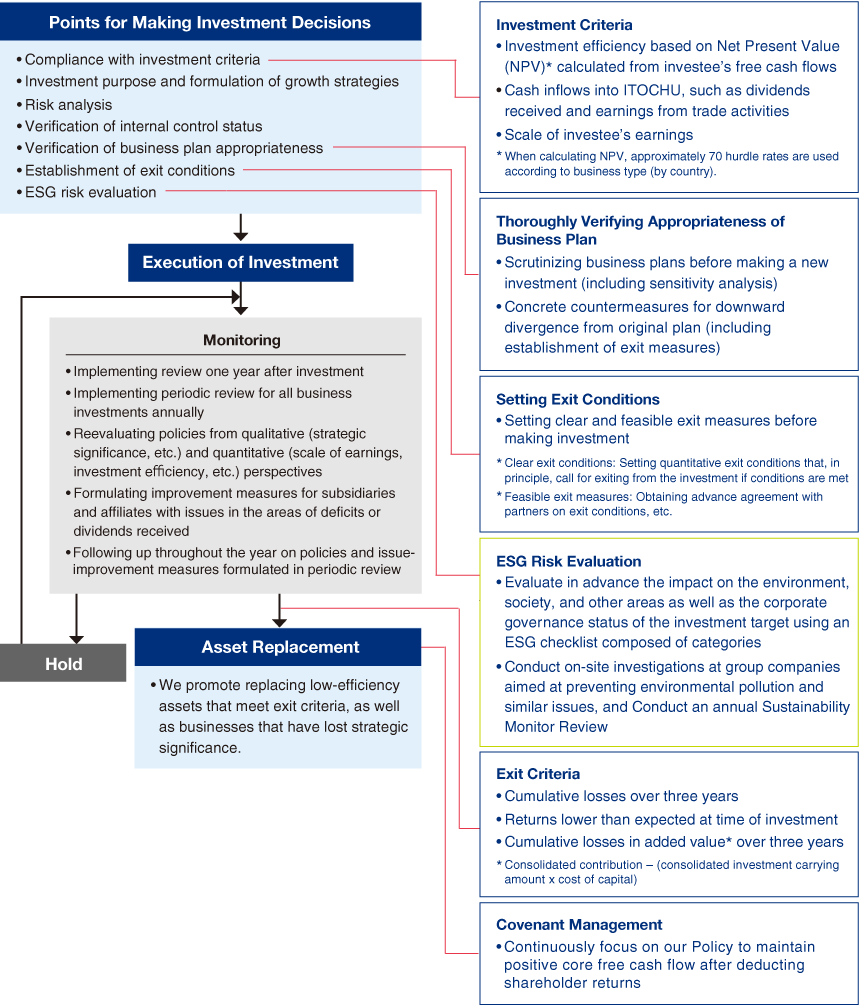
Along with strategic business alliances, business investment is an important means of creating new businesses. To actively promote strategic investments in areas of strength in a timely manner, we choose the optimal structure from a wide range of methods, such as establishing a wholly owned subsidiary, implementing joint investment with partners, and participating in management through M&As or converting to a consolidated subsidiary.
In principle, we hold investments continuously. After making each investment, we work to maximize the investee’s corporate value and to expand trading profit and dividends received by fully utilizing our Groupwide capabilities. Given such considerations as larger-scale investments in recent years, we are rigorously screening the appropriateness of the business plan and acquisition price. For existing investments, to increase investment earnings and to exit quickly from low-efficiency assets, we are further strengthening monitoring procedures, centered on instituting more rigorous exit criteria and thoroughly implementing periodic investment review.
Decision-Making Process for New Investments
A multilayered decision-making process that achieves quick decision-making by giving a certain level of discretion to the Division Companies while striving to pursue investment return and curb investment risk.
Regarding investment risks, the risk appetite is determined by considering factors such as market growth and stability, the impact on our company’s performance, and the feasibility of risk management.
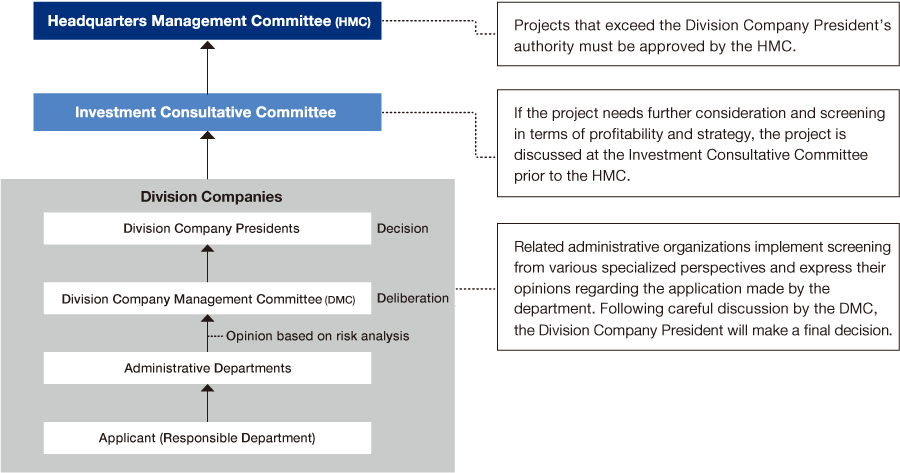
Business Investment Process
Starting with the impact of COVID-19, the business environment changed dramatically.
Against this background, we steadily implemented strategic investment at the right time and divested businesses which are less efficient or past the peak.
At the same time, we strictly implemented various processes, including the verification of the validity of business plans at the time of investment decisions, and meticulously monitored those decisions after investing. This allowed us to maintain a high ratio of profit-making Group companies at 91.6% in FYE 2025.
Number of Consolidated Subsidiaries and
Share of Group Companies Reporting Profits

Security Risk Management
Policy and Basic Concept
Protecting our information assets from threats such as loss, alteration, leakage, and unauthorized use and ensuring their proper handling is indispensable for our sustainable growth of our business activities. All internal policies and rules regarding information handling, including the Code of Conduct, must be strictly adhered to by all executives and employees. This commitment has been publicly disclosed as our Information Security Policy. Additionally, when commencing the outsourcing of information system development, maintenance or other related services, it will be verified whether the company/partner meets the requirements established by ITOCHU Corporation. All officers and employees are dedicated to handling, managing, protecting, and maintaining information strictly accordance with our policies.
Structures and Organization
The Chief Transformation Officer (CXO) is appointed as the executive responsible for overseeing IT and digital transformation, information security and cybersecurity strategy. Under the leadership of the CXO, the IT Strategy Committee deliberates not only on comprehensive IT and digital strategies but also on strategic measures related to information security and cybersecurity. In addition, discussions on various policies and regulations, as well as the monitoring of these initiatives, are conducted. These topics and discussions are regularly reported to the Board of Directors, thereby ensuring that the robust information security is maintained.
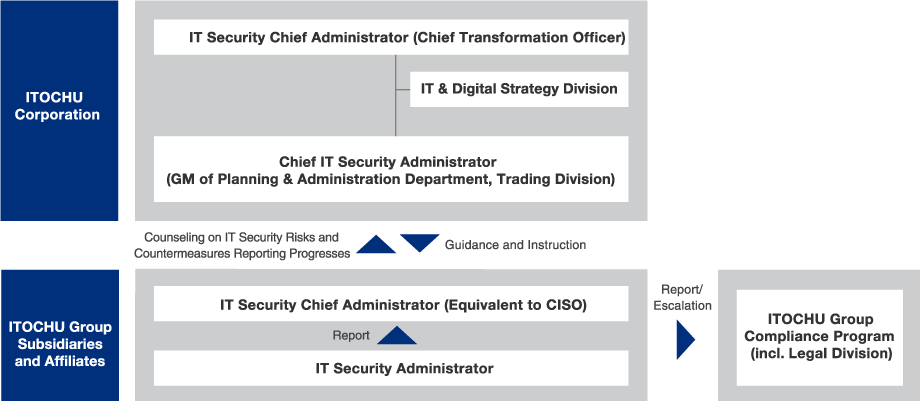
| Name | Chairman | Objectives |
| IT Strategy Committee | Chief Transformation Officer (CXO) |
|
Initiatives
ITOCHU Group leverages IT and digital technologies to drive our business operations. To maintain the robust information security that underpins these operational foundations, we are committed to continuously strengthening our information security through the refinement of policies, the expansion of our infrastructure, and the sustained, effective operation of robust security measures.
ITCCERT (ITOCHU Computer Emergency Readiness, Response & Recovery Team) tirelessly gathers threat intelligence through various resources, this enables us to prevent incidents before they occur and, if any cyber incidents arise, to execute incident response (root cause analysis, developing countermeasures, and restoring services) immediately. The ITOCHU Group Cybersecurity Framework has been rolled out globally since 2022 as our cybersecurity governance framework. Under this framework, each Group company defines its own policies, organizational structure, and processes to further bolster its cybersecurity posture. Furthermore, in February 2023 we founded ITOCHU Cyber & Intelligence Co., Ltd. (ICI). Through ICI, Cybersecurity Countermeasures Program has been delivered to all Group companies, ensuring the framework’s sustained and practical operation. As examples of specific measures, we have implemented the following initiatives:
- To assess the security measures of each Group company, Red team exercise are conducted in which security experts, acting as threat actors, simulate cyberattacks simulate cyberattacks.
- Cybersecurity risk assessments and annual compliance verifications against the Information Security Minimum Standard, which consolidates the Group’s essential baseline security rules, are conducted each year.
Furthermore, we have instituted a group-wide training program for the education and development of cybersecurity specialists. As a result, compliance breaches, including data leakages, have been limited to only a handful of incidents per year across the Group (two cases in FYE2025). Few companies in Japan have been as proactive in building robust structures and engaging so actively in these efforts. We will continue to advance initiatives that underpin our sustainable growth.
Additionally, the following training activities are conducted regularly to maintain and enhance our information security management posture.
- Phishing email training for all employees (biannual)
- Every three years, an e-learning-based training Information Security Course is provided for all Group-company employees.
- Comprehensive information-security and personal-data-protection briefing are provided at onboarding process. In case there are any policy renewals, updated training programs are delivered to all Group-company employees.
- ITCCERT-led information-security workshops and seminars for ITOCHU Group companies on ad-hoc basis
- An annual drill is conducted to ensure the effectiveness of our business continuity plan (BCP). Third-party cyber-attack simulation exercises are conducted at least once a year.
Lastly, for the appropriate usage and development of generative AI, which has proliferated rapidly in recent years, we have established and are enforcing guidelines that ensure proper information handling, respect for privacy, bias avoidance, and the identification of AI-generated content.
Business Continuity Plan
Please refer to Business Continuity Plan in Internal Control System for details.

